Have we passed peak health care disruption?
Have we passed peak health care disruption?
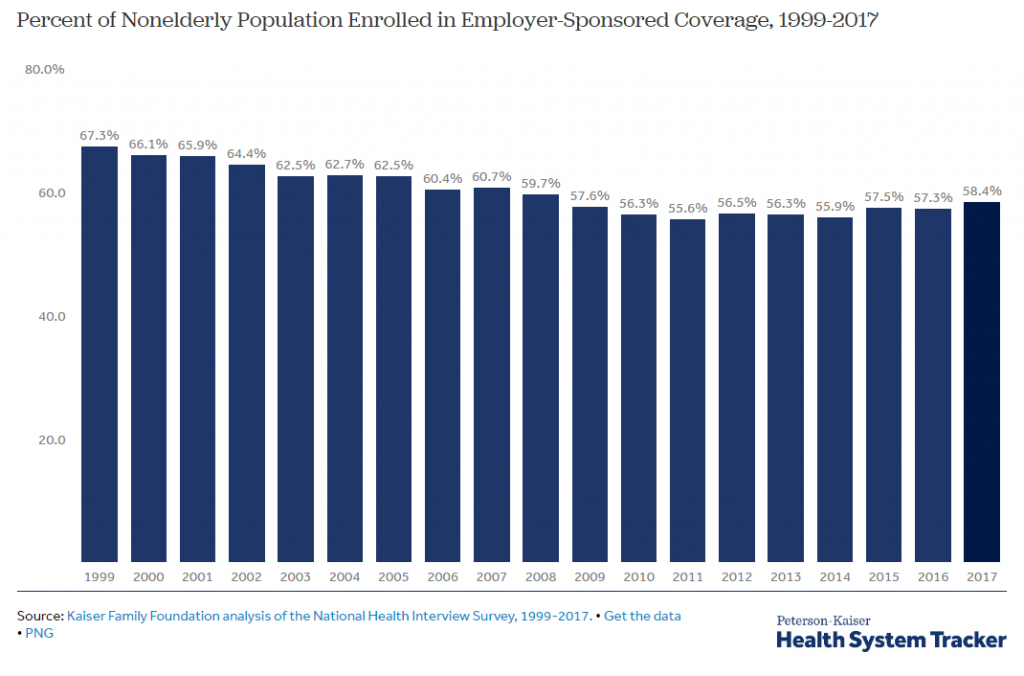
Disrupting health care has been a hot topic the past few years, but it seems to me we have passed peak health care disruption and firms are now having to roll up their sleeves to do the boring, difficult work of creating incremental change.
The high point of disruption in health care (see chart below) looks to be the announcement January 30, 2018 from Amazon, Berkshire Hathaway, and JPMorgan Chase & Co. of a health care joint venture to “address healthcare for their U.S. employees.”
What has happened related to that partnership in the last 18 months is the naming of the entity (Haven), some prominent hires (Dr. Atul Gawande), and some key staff departures (Jack Stoddard).
But there have been some notable smaller steps from two of the three Haven entities that signal feasibility and immediate impact are stronger drivers than disruption. While policy types may be interested in wholesale transformation, the business of digital health is concentrated on more immediate change.
Right after the Haven announcement, Amazon bought PillPack, an online pharmacy and platform that helps manage patient data. Last month, JPMorgan Chase & Co. bought InstaMed, adding health care payment services to the bank’s existing service offerings in wholesale payments. Knowing more about your customer and serving them better, just like in any other business, seems to be where health care companies are focused.
These kinds of digital health deals may be the wave of the future, according to RockHealth’s 2019 Midyear Digital Health Market Update. Their report (see chart below) shows a steady amount of digital health investing year-over-year, but an increasing average deal amount.
Perhaps more importantly, acquisition by non-health care companies is proving to be an increasingly likely exit ramp for digital health investors, as the PillPack and InstaMed deals exemplify. Providers and non-health care companies are stepping up their acquisitions of digital health ventures, as the chart below shows.
The next step in health care might be smaller than the word “disruption” implies. Over the past few years, health care has proven to be more complex than many tech companies and policymakers have thought. RockHealth quotes David Kim, Managing Director of DigiTx Partners, as saying: Big tech companies “are likely to acquire technologies and companies with expertise and domain knowledge that allow them to take that next step to health care without just diving in blindly headfirst.”
If disruption equates to diving in blindly headfirst, I agree. Health care change going forward is going to be data-fixated, consumer-focused, and incremental.